As one of the most competitive global industries, the automotive industry relies on cutting-edge technologies such as additive manufacturing for optimized efficiency and increased productivity. Most automotive manufacturers typically integrate additive manufacturing technology in the automotive manufacturing process to speed up prototyping and encourage design flexibility and customization.
Although additive manufacturing provides a competitive edge and production flexibility for automotive parts, it is important to understand the technology to achieve better outcomes. This article will explore additive manufacturing technology, its processes, advantages, and limitations in the automotive sector.
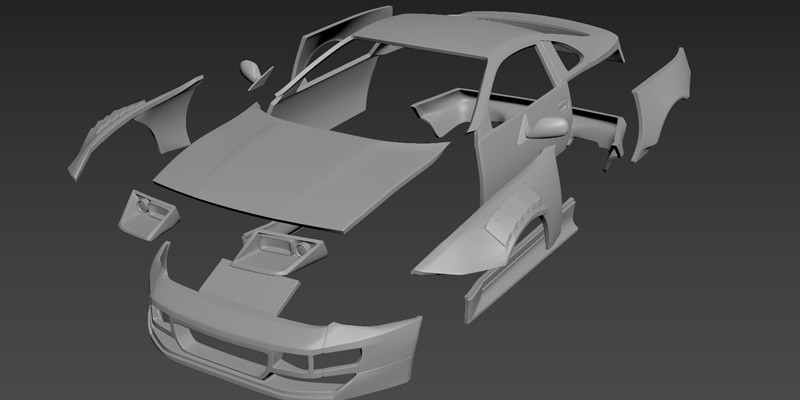 What is Additive Manufacturing?
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive Manufacturing, otherwise known as 3D Printing, encompasses various technologies, including fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), digital light processing (DLP), direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), and many more.
This manufacturing processes create three-dimensional (3D) components from a digital file layer by layer until the finished part’s desired shape or geometry is achieved. Unlike subtractive manufacturing processes, this technology adds material in the required amount to achieve the desired product. Commonly, It is compatible with materials such as composites, plastics, resins, etc.
Different Additive Techniques Used in the Automotive Industry
The AM technology is a versatile and reliable automotive parts manufacturing process. Although it can produce structurally complex prototypes and parts for testing and verifying functionality, it doesn’t work well with high production runs.
Automotive manufacturers typically use this technology in the product development phase to create 3D-printed parts from CAD designs. Here are the primary additive manufacturing techniques that they utilize in making automotive parts:
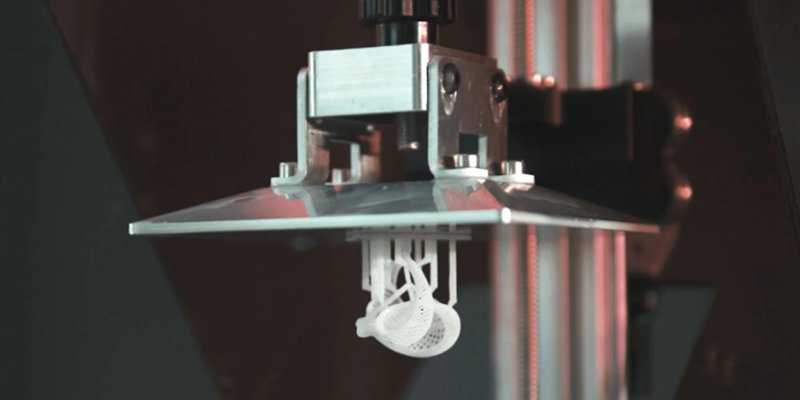 Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography involves curing photopolymer layers to produce desired automotive parts one layer after another. The process exposes each photopolymer layer to a UV laser to cure and bond it to the previous layer until it forms the desired product. Due to its precision, printing accuracy, and intricacy, manufacturers often use this process to make vehicle components like light covers, dashboard components, and seat frames.
 Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
This AM process uses a laser to sinter or bind fine powder to create solid automotive parts like battery covers, single-part control panels, brackets, and clips. Machinists create the final object by focusing the 3D printer’s laser at specific points of the powder bed, causing an atomic reaction that bonds the material powder’s particles into a solid object. The SLS technique boasts printing precision and isotropic strength when creating various automotive components.
 Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is a common AM technique that creates automotive parts by extruding layers of thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle onto a build plate to create an intended product. Automotive engineers use the FDM technique to create cheaper parts with high strength and dimensional stability, such as prototyping parts, dashboard mounts, etc.
Digital Light Process (DLP)
Digital light processing uses a projected light source to harden or cure an entire media layer. The ability to fabricate intricate designs and the speed and precision of the process make it a suitable manufacturing technique for making small, intricate vehicle components like custom interior components.
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
This process involves applying fusing and detailing agents to a powdered thermoplastic bed using an inkjet array and heat to bond each layer. Automotive manufacturers use this MJF process to create sturdy, functional prototypes and parts like lights and air ducts for mechanical testing.
PolyJet
Polyjet develops layers of curable liquid photopolymer onto a build platform and cures it with UV light to create functional, high-resolution automotive parts with desired aesthetic properties. Automotive manufacturers use the polyjet process to create multi-color and multi-material vehicle parts like interior components, custom fixtures, and prototypes that require rubber-like materials.
 Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
DMLS works similarly to SLS since it focuses a laser on the powder bed at specific angles within the space to form each layer. Then, the printer spreads metal powder for the next layer and repeats the process after completing each layer. DMLS can fully melt particles together to ensure stable mechanical and material properties. Automobile manufacturers use the DMLS process to make metal components like suspension springs, thanks to the process’s consistency and repeatability after a successful print.
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
The electronic beam melting process uses a high-power beam of electrons guided by a magnetic field to melt powdered metal layer by layer in a vacuum chamber. The process’s speed, accuracy, and strength of fabricated parts are typical benefits of EBM.
Additive Manufacturing Benefits For Automotive Part Manufacturing
Here are the expected benefits of incorporating additive manufacturing into their strategies for making automotive components:
Rapid Prototyping
Prototyping is an integral aspect of the automotive parts design and manufacturing process. Product designers often use accurate, scale prototypes to test performance, fit, and aerodynamics and to communicate design ideas between production teams. A physical model for each product variation helps identify potential design issues and simplify comparing versions, allowing automotive designers to optimize products accurately, meet performance requirements, and improve aesthetics.
Additive manufacturing allows automotive designers to simulate various parameters before printing. Thus, it reduces the required number of iterations before production and fast-tracking development. With additive manufacturing, product teams can easily create prototypes of molds, jigs, and fixtures on-site, as well as thermoforming tools and grips.
 Ease of Customization
Ease of Customization
Additive manufacturing processes support the production of custom vehicle parts. You can 3D print custom parts on a driver-by-driver basis, and the technology allows you to produce unique parts for vintage car models. For instance, you might use additive manufacturing processes to create personalized aesthetic vehicle components.
Furthermore, you can make customized car assembly tools with additive processes to ensure seamless production of high-quality automotive parts. These customized assembly tools should work better than mass-produced tools, facilitating optimized productivity down the line.
Weight Reduction
Additive manufacturing allows the use of lightweight materials like plastic, composites, carbon fiber, and light metals with relatively low density in manufacturing optimized automotive structures and parts such as suspension systems, engine components, seats, dashboards, and door panels.
Lightweight 3D-printed automotive parts help significantly reduce car weight and emissions and improve safety without compromising functionality. Moreover, lighter parts help automotive manufacturers ensure fuel efficiency in gas-powered vehicles.
Lesser Material Waste
Generally, additive techniques use fewer materials since you only need the required amount of material to build each layer of the desired part. Hence, it significantly reduces material waste rather than subtractive processes that remove material from a larger block. Moreover, several additive techniques encourage sustainability and less material waste by allowing you to reuse excess or unused raw materials.
Simplified Supply Chain
Additive manufacturing processes such as 3D printing help simplify the automotive industry’s supply chain. The supply chain of many automotive companies is highly complex due to the reality of outsourcing different parts. Additive technology allows manufacturers to print vehicle parts near the final assembly facility, reducing waste, downtime, and associated shipping costs.
Cost-effectiveness
When compared to traditional manufacturing, additive manufacturing yields a positive return on investment. With additive manufacturing, replicating car parts is highly cost-effective since it reduces molds, tooling, and setup costs common to customized products or small production runs.
Moreover, the automation of additive manufacturing processes reduces labor costs by mitigating potential human errors. Also, additive manufacturing’s on-demand production capability helps lower inventory costs by reducing the need to manage large inventories.
 Challenges of Additive Manufacturing in the Automotive Industry
Challenges of Additive Manufacturing in the Automotive Industry
Although additive manufacturing allows greater efficiency, sustainability, and innovation in the automotive industry, here are some of the challenges automotive manufacturers face with this technology.
High Initial Costs
Additive manufacturing has higher upfront costs since the printing equipment and specialized materials like metal powders and high-performance polymers used in additive manufacturing can be quite expensive. Thus, the technology becomes unaffordable for small-scale businesses. Moreover, additive manufacturing requires training personnel with the latest software to use the equipment efficiently.
Size Limitations
Most 3D printing systems have restricted build volumes, limiting the size of automotive parts they can create in a single piece. Large automotive components often demand significant post-processing, which can be burdensome and time-consuming. Consequently, this leads to an increase in complexity and production costs.
Multi-material Printing
Despite the prowess of Additive manufacturing technology, automotive manufacturers experience setbacks when printing different materials simultaneously. Integrating and bonding these materials into a single print can be complex due to material compatibility. Since extensive testing and validation are required, ensuring that a part with multiple materials meets the required performance standards and material properties can be challenging.
Unsturdy and Poor Durability
The additive technology’s layer-by-layer building process sometimes creates parts that are not sturdy and have weak points between the connected layers. Although compatible with a wide range of materials, AM processes sometimes use materials with inferior strength and durability, which can degrade over time. Moreover, these 3D-printed automotive parts can be susceptible to environmental factors like UV exposure, heat, and chemicals.
Slower Production Rate
Generally, additive manufacturing processes are more time-consuming and limited by production speed and build size. 3D printing parts is especially slow because each layer needs to be deposited and cured individually. Thus, achieving desired automotive parts with additive manufacturing processes takes longer. Besides, automotive manufacturers might experience difficulty scaling up production to meet the industry’s quantitative requirements.
 Automotive Product Stages Where AM Can Help
Automotive Product Stages Where AM Can Help
Due to the unique benefits of additive manufacturing, here are automotive product stages where additive manufacturing can offer changes.
From Concept to Prototypes
Since prototyping can take substantial time in product development cycles and become expensive due to multiple iterations, AM helps automotive manufacturers quickly transform ideas into reliable validation concepts. These concepts transition to highly precise prototypes that meet the requirements and guide automotive products through more iterations and validation stages till the product is ready for mass production.
With 3D printing, you can achieve highly accurate prototypes at much lower cost and within a few days, optimizing the overall product development workflows.
Repair and Maintenance
3D printing car parts eliminates the need to maintain inventory since you can store all designs for various parts as a digital copy on a computer hard drive. Additive technology allows you to produce any spare parts on demand. The accessibility of additive manufacturing processes encourages automotive manufacturers to 3D print car parts and spare parts easily. They can even reproduce very old parts through the digital scanning of existing parts.
Customization
While customization can be time-consuming and relatively expensive with traditional manufacturing processes, additive manufacturing offers an ideal, low-cost solution for parts customizing. It allows automotive manufacturers to produce cost-efficient customized parts, enabling new capabilities in what they can create and provide prospective customers.
AutoProtoWay Offers Innovative Manufacturing Solutions for Your Automotive Projects
AutoProtoWay offers additive and subtractive manufacturing services for automotive prototyping and part manufacturing. By integrating additive manufacturing into the production process, we can help you accelerate prototyping, enhance design flexibility, and achieve higher customization. Partner with AutoProtoWay to leverage innovative machining solutions for your automotive projects, ensuring the new products move to market fast.
Conclusion
Additive manufacturing technology remains a driving innovation in the automotive industry, introducing new design, production, and customization possibilities. While the automotive industry embraces additive technology to improve production speed, and precision and reduce costs, several challenges are associated with the processes.
FAQs
What are the typical parts AM is used for in the automotive industry?
Automotive manufacturers often use additive manufacturing processes to create reliable prototypes, production parts, tooling, and spare parts for different vehicles.
What are the standards or regulations for additive manufacturing in the automotive industry?
To ensure quality, reliability, and safety, manufacturers in the automotive industry manufacture 3D-printed parts to meet certain industry-specific standards and certifications, such as ASTM, ISO, and SAE International.




