From a part manufacturer’s point of view, a car is made up of several systems coming together to provide the best driving experience. Each system has its function, an example is this article’s object, the automotive water pump.
However, many are unsure how the car water pump functions. This article will discuss the automotive water pump, including its functions, types, applications, and manufacturing process.
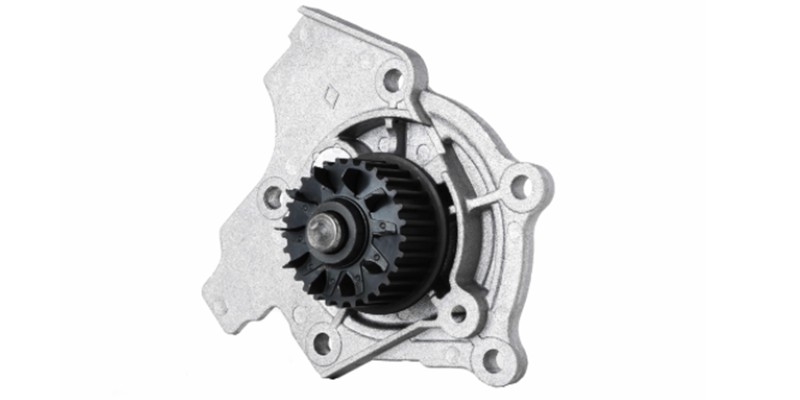 What is a Water Pump in the Car?
What is a Water Pump in the Car?
The automotive water pump is a core automotive component that includes the camshafts, gearbox, and fuel system. It is one of the car cooling system components that primarily functions in pushing water or coolants in the car radiator to the car heat generating systems such as the engine before the water returns to the radiator. Doing so, it picks up the heat generated by the engine and these different parts, dissipating in the radiator via convection assisted by the radiator fan.
The car water pump can be located externally on the engine or flanged on the engine block. Those pumps fitted externally on the engine are driven by the car belt that drives additional components such as the generator and servo pump. On the other hand, flanged automotive water pumps are however driven via the timing belt of the valve control system.
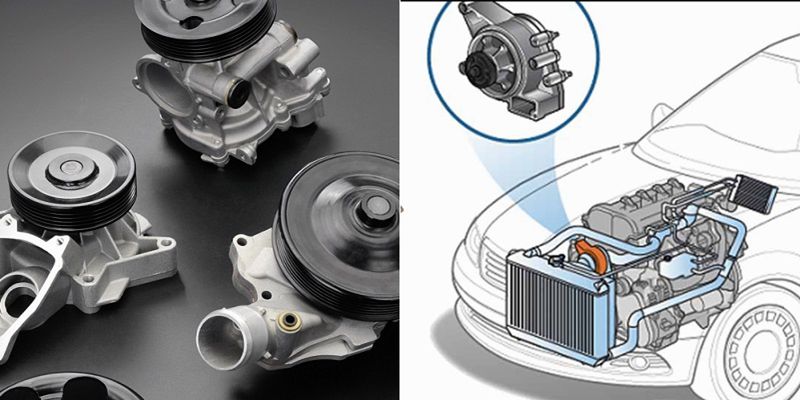 Functions of Automotive Water Pumps
Functions of Automotive Water Pumps
The automotive water pump, apart from pushing the coolant in the radiator services many functions as highlighted below:
Generating Water Pressure
The primary function of the car engine pump is to generate the water pressure that pushes the water and/or coolants in the radiator through the coolant system into the engine and other parts and back to the radiator.
Temperature Regulation
Generating the pressure to push the water leads to the second function which is temperature regulation. Without an engine water pump, the water in the radiator is static but by pumping water, the pump prevents the engine and other heat-generated systems from severe damage due to overheating.
Lubricating the Shaft and Bearings
Some car engine pumps can lubricate the shaft and bearings, reducing friction and mechanical wear. Without proper lubrication, the shaft and bearings face increased resistance which can offset engine performance.
Sealing the Cooling System
Some car engine pumps seal the cooling system to prevent coolant leaks. As a result, there is efficient thermal regulation. A compromised seal will cause coolant leaks, leading to overheating and engine damage.
Driving the Timing Chain
In flanged water pumps, the water pump drives the timing chain or belt, aligning the movement of the engine’s valves and pistons. As a result, there is optimum engine functionality, ensuring the valves open and close at the correct intervals.
 How Does a Car Water Pump Work?
How Does a Car Water Pump Work?
The automotive water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine using a simple mechanism. The inlet port receives water or coolant from the radiator, and inside the pump housing, the impeller blade spins, generating centrifugal force that pushes the coolant outward into the cooling channel. Doing so, the coolant exits the pump housing through the outlet port.
The mobile coolant then flows into the car engine and cylinder head, absorbing the combustion-generated heat. It can also move to other parts depending on the car. Afterward, it returns to the radiator, dissipating the absorbed heat via convection aided by the radiator fan.
The other car engine pump components also smoothen the pumping process. This continuous cycle of coolant circulation ensures the engine operates within a safe temperature range, optimizing performance and extending the vehicle’s lifespan.
Types of Car Water Pumps
Generally, car water pumps depend on performance and reach, which proves why passenger cars and trucks have different types. The four categories include:
Electric Water Pumps
Electric water pumps create a supply flow independent of the motor’s number of revolutions. As a result, they reduce power requirements, fuel consumption, friction, and pollutant emissions.
Mechanical Water Pumps
Depending on the construction, mechanical water pumps are installed on or mounted on the engine block. Unlike electric water pumps, they are driven by timing belts, V-belts, or the engine.
Auxiliary Water Pumps
The auxiliary water pumps support the main water pump of an automobile. They are located in the main cooling system’s bypass hose, and some automobiles can have more than one cooling system. Based on their structures, they are found in hybrid and electric vehicles, distributing coolant to all corners of the vehicle’s system.
Variable Water Pumps
Variable water pumps can adjust the flow rate based on the car engine demand, carried out by a vacuum process. This means the water pump can only work when required. As a result, it improves engine efficiency and reduces fuel consumption and pollutant emissions.
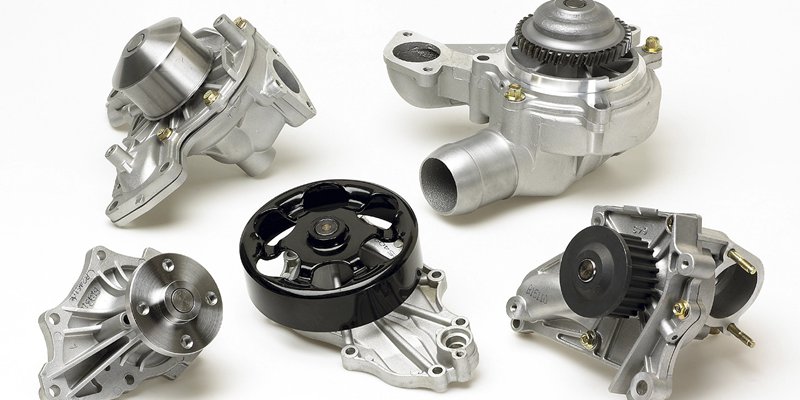 Components of an Engine Water Pump
Components of an Engine Water Pump
Regardless of the type of car, every automotive water pump system has a base number of components, which include the following:
Pump Housing
The pump housing a car water pump component is made from cast aluminum, iron, or sometimes reinforced plastic for high-end cars that must maintain a lightweight. It has an inlet and outlet port for the coolant to enter and exit and functions as a housing for the other components.
Impeller
The impeller is made from metals like stainless steel or aluminum. It features a fan-like rotor with vanes or blades that spin, creating a centrifugal force that propels the coolant through the cooling system.
Shaft
The shaft connects the impeller to the drive mechanism, which, depending on the car, can be a pulley or an electric motor. This ensures that the impeller rotates smoothly.
Bearings
The bearing (ball or roller bearings) supports the shaft, providing stability and reducing friction during operation. Additionally, it ensures longevity under high-speed rotation and pressure.
Seal
The seal is made from a heat-resistant material such as rubber or silicone and has a spring-loaded mechanism for tight sealing the coolant. As a result, it prevents the leakage of coolants.
Pulley or Drive Mechanism
The puller or drive mechanism drives the pump. On the one hand, the pulley is connected to the engine’s serpentine or timing belt, while the electric motor powers the pump without a belt.
Inlet and Outlet Ports
From their names, the inlet port receives coolant from the radiator while the outlet port sends it to the engine block for circulation.
Weep Hole
The weep hole is located between the pump housing and the bearing assembly. It is used to drain excess coolant in case of seal failure. Additionally, it is a warning sign of wear as a leak indicates potential car water pump issues.
 Different Manufacturing Processes for Automotive Water Pumps
Different Manufacturing Processes for Automotive Water Pumps
The processes for manufacturing an automotive water pump depend heavily on the subcomponents and the project requirement. Typical manufacturing processes you can rely on include:
Metal Casting
Metal casting is a material preparation process but can also be the right process for manufacturing automotive water components like pump housing. The most common metal casting techniques in this regard are die casting and sand casting.
Due to its efficiency, die casting is the preferred method for complex metal components. In contrast, sand casting is the better choice for components made from materials like iron.
Metal Forming
Metal forming techniques such as stamping and forging are used for high-strength and durability components. Stamping is used to fabricate metal pulleys and impeller blades from stainless steel sheets. Shafts are forged and then machined to enhance strength and fatigue resistance.
CNC machining
Aside from being suitable for rapid prototyping and manufacturing cylinder heads and crankshafts, CNC machining techniques, like CNC milling, turning, drilling, etc., are the ideal options for the precision manufacturing of water pump components.
Using CNC machining techniques, you can achieve tight tolerances. Hence, they are the process of choice in drilling inlets and outlets and manufacturing impellers, shafts, and housings.
Surface Treatments
After manufacturing, you can subject the automotive component to a surface treatment process, such as anodizing, heat treatment, powder coating, annealing, etc., to enhance durability and resistance to wear, corrosion, and heat.
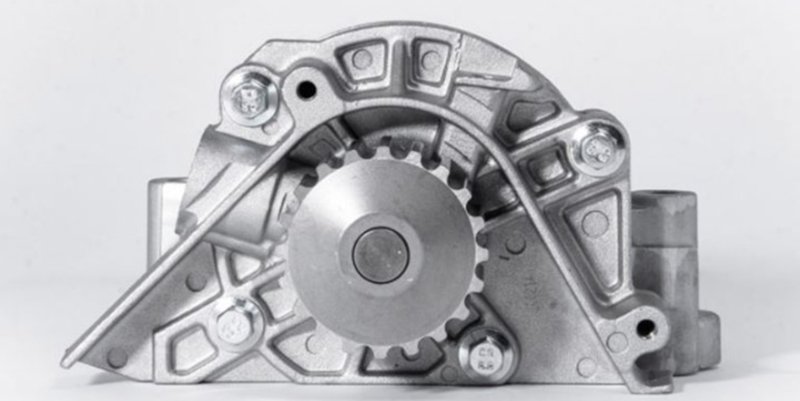 How to Maintain Vehicle Water Pump?
How to Maintain Vehicle Water Pump?
The vehicle water pump requires maintenance which can make it last for the entire life of a car. So, take good care of the pump using the tips below.
- Avoid a Dry Run: Running a water pump without coolant, known as a dry run, can damage the engine and water pump system. The circulation of the coolant aims to regulate engine temperature and lubricate/cool the pump’s internal components, such as seals and bearings. Without this, it can lead to severe damage.
- Regularly Check the Cooling Components: Check other components of the car cooling system such as the coolant, radiator, and thermostat regularly. Also, always maintain the correct engine coolant level to keep the engine cool and safe from damage.
- Stop Using Improper Coolant: Avoid using contaminated coolant, mixing coolant of different chemistries, or using non-compatible coolant with your vehicle. The presence of contaminants will affect the seals and form pathways for leakage. Non-compatible coolants cannot protect the components from rust and corrosion.
- Avoid Defective Belt: There is an important relationship between the water pump and the belt that drives the system. Hence, if you are changing the water pump, replace the belt also to minimize the risk of premature failure of both components.
- Regularly Check the Coolant Level: Keep an eye on the engine coolant level and refill it as needed. Low coolant levels can lead to overheating the engine and compromise the pump’s performance. Additionally, check signs of leaks in the cooling system which can contribute to a lower coolant level.
WayKen’s Expertise in Automotive Custom Parts Machining
WayKen specializes in producing custom automotive parts with precision and efficiency, using advanced machining techniques for complex components like water pumps. We offer one-stop custom manufacturing services, including CNC machining, die casting, and sheet metal fabrication, ensuring tight tolerances and high-quality results. WayKen delivers reliable components that support your automotive systems, enhancing your product development process.
Conclusion
The automotive water pump is a core component of the cooling system that maintains engine performance through temperature regulation, prevention of engine leaks and in some car engines, driving the timing chain or belt for the engine’s valves and pistons synchronization.
FAQs
How long does an OEM water pump last?
An OEM automotive water pump has a longevity between 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
How is quality ensured in the manufacturing of automotive water pumps?
Quality assurance in automotive water pump manufacturing includes material testing, dimensional inspections, and surface treatments. Leak testing, for example, can identify seal or housing failures.
Which part of the water pump becomes worn out fast?
The impeller is the water pump part that wears out fast. It creates the flow and pressure of water and damage to it can reduce the water flow.




